Sustainable transport is no longer a niche or experimental domain: it is becoming the backbone of European urban transformation. In May 2025, a range of developments across cities and institutions have reaffirmed Europe’s determination to rethink how people and goods move. From revised emissions regulations to bold urban initiatives and pioneering technologies, this month has showcased a variety of ways in which change is being driven: through policy, innovation and citizen engagement. Here’s a curated overview of the most impactful news from the past weeks.
EU Relaxes CO₂ Emission Targets for Automakers
On May 8, 2025, the European Parliament voted to ease CO₂ emissions targets for carmakers, allowing them to average emissions over the three years from 2025 to 2027. This revision comes in response to industry concerns over the pace of EV transition, compounded by global competition and slower-than-expected consumer adoption.
The decision has sparked contrasting reactions. While car manufacturers welcomed the regulatory flexibility, many environmental groups criticized the move, warning that it may delay progress toward Europe’s 2030 climate goals.
This shift reflects the delicate balance EU lawmakers must strike between industrial competitiveness and ecological responsibility.
Edinburgh Reconsiders Congestion Charge
Nearly 20 years after its first proposal was rejected by referendum, Edinburgh is once again debating a congestion charge. The aim? To reduce private car usage by 30% by 2030 and fund urgently needed improvements in public transport.
Council leaders say the situation today is markedly different than in 2005: growing climate awareness, new low-emission targets, and increased pressure on urban infrastructure make the case for congestion pricing more compelling. Still, the idea remains politically sensitive and public opinion divided.
Edinburgh Launches “Tap on, Tap off” Tram Payments
In a more tangible step forward, Edinburgh officially launched its new “Tap on, Tap off” (ToTo) contactless payment system on May 19. The technology allows commuters to tap their card or mobile device at the start and end of a tram journey, with the system automatically applying the best fare based on travel frequency.
This move is part of a wider strategy to modernize the city’s public transport system, reduce ticketing barriers, and make sustainable mobility more accessible to both residents and visitors. Authorities hope the ease and flexibility of the ToTo system will encourage more people to choose public transport over private cars.
Paris Introduces Car-Sharing Lane on the Périphérique
Paris continues its push to reduce traffic and emissions with a dedicated car-sharing lane on the périphérique. This new policy aims to prioritize high-occupancy and shared vehicles during peak hours, discouraging solo drivers and easing congestion.
Infractions are subject to a €135 fine, and enforcement is managed through smart camera technology. The lane forms part of a broader strategy that includes expanding low-emission zones and investing in public transit infrastructure, reaffirming Paris’s role as a frontrunner in urban mobility reform.
France to Pilot the First Electric Highway Segment
In one of the most exciting technological initiatives of the month, France confirmed its plan to launch a pilot segment of an “electric highway” on the A10 autoroute. The project uses inductive charging coils embedded in the road surface to wirelessly power electric vehicles as they drive, potentially eliminating the need for frequent charging stops.
The trial, expected to begin in late 2025, will test the feasibility of scaling such technology nationwide. If successful, it could play a significant role in supporting long-distance EV travel and reducing range anxiety, a major barrier to electric vehicle adoption.
Micromobility and Transport Poverty: A Social Climate Priority
Shared bikes, e-scooters, and micromobility services aren’t just for tech-savvy urbanites. As argued by Cycling Industries Europe and Micro-Mobility for Europe, these tools can directly address transport poverty by providing affordable and flexible mobility for vulnerable groups.
In May, both organizations jointly called for the creation of a Social Climate Fund to help integrate micromobility into EU-level sustainability and equity strategies. Their proposal includes subsidies for low-income users and targeted investments in underserved areas. Micromobility, they argue, can be a low-cost, high-impact solution to transport inequality.
Final Thoughts
The stories from May 2025 illustrate how Europe is driving the shift to sustainable mobility; not just through grand gestures, but through strategic and often localized action. Whether it’s rethinking road pricing, investing in inclusive mobility or testing groundbreaking technologies, one theme is clear: the future of transport is not only electric, but shared, smart, and deeply human-centric.

















 making it easier than ever to connect individuals who have resources with those who need them. From renting a car for a few hours to sharing office spaces, the sharing economy is broadening access while reducing waste.
making it easier than ever to connect individuals who have resources with those who need them. From renting a car for a few hours to sharing office spaces, the sharing economy is broadening access while reducing waste.


 The European Commission has introduced a legislative proposal aimed at regulating peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and crowdfunding platforms. This initiative seeks to enhance access to financing for innovative businesses while ensuring transparency and consumer protection. By establishing a standardized framework, the EU aims to create a fair and competitive environment for companies operating in the collaborative finance sector.
The European Commission has introduced a legislative proposal aimed at regulating peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and crowdfunding platforms. This initiative seeks to enhance access to financing for innovative businesses while ensuring transparency and consumer protection. By establishing a standardized framework, the EU aims to create a fair and competitive environment for companies operating in the collaborative finance sector. The integration of blockchain technology into the sharing economy is accelerating, leading to the rise of decentralized platforms offering services such as car-sharing, home-sharing, and freelance work. These platforms leverage blockchain’s inherent security and transparency to provide users with greater control and reduced costs. For instance, projects like Bittensor (TAO) are developing decentralized networks that combine artificial intelligence and blockchain to foster open and collaborative ecosystems.
The integration of blockchain technology into the sharing economy is accelerating, leading to the rise of decentralized platforms offering services such as car-sharing, home-sharing, and freelance work. These platforms leverage blockchain’s inherent security and transparency to provide users with greater control and reduced costs. For instance, projects like Bittensor (TAO) are developing decentralized networks that combine artificial intelligence and blockchain to foster open and collaborative ecosystems.  Several global cities are piloting shared autonomous vehicle (SAV) programs within designated urban areas. These initiatives aim to alleviate traffic congestion and reduce emissions by offering affordable and efficient transportation alternatives. The successful implementation of SAVs could revolutionize urban mobility, making cities more sustainable and interconnected.
Several global cities are piloting shared autonomous vehicle (SAV) programs within designated urban areas. These initiatives aim to alleviate traffic congestion and reduce emissions by offering affordable and efficient transportation alternatives. The successful implementation of SAVs could revolutionize urban mobility, making cities more sustainable and interconnected. Sustainability remains a central focus in the evolution of the sharing economy. Investments are pouring into projects that promote environmental consciousness, such as reusable packaging programs, clothing rental services, and repair-sharing platforms. With consumers increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly options, businesses that incorporate sustainable practices into their sharing models are poised for success.
Sustainability remains a central focus in the evolution of the sharing economy. Investments are pouring into projects that promote environmental consciousness, such as reusable packaging programs, clothing rental services, and repair-sharing platforms. With consumers increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly options, businesses that incorporate sustainable practices into their sharing models are poised for success.
 Owning a personal vehicle comes with high costs, including fuel, insurance, maintenance, and parking fees. Shared mobility alternatives like car-sharing and ride-sharing services allow people to access transportation only when needed, significantly lowering expenses. Additionally, shared mobility options offer flexibility, eliminating the long-term financial commitment of owning a vehicle while ensuring reliable and affordable transport solutions.
Owning a personal vehicle comes with high costs, including fuel, insurance, maintenance, and parking fees. Shared mobility alternatives like car-sharing and ride-sharing services allow people to access transportation only when needed, significantly lowering expenses. Additionally, shared mobility options offer flexibility, eliminating the long-term financial commitment of owning a vehicle while ensuring reliable and affordable transport solutions. Personal vehicles contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. Shared mobility services help combat climate change by encouraging people to use environmentally friendly transport options like electric car-sharing, bike-sharing, and e-scooter programs. Many cities are integrating shared electric vehicle fleets and expanding cycling infrastructure to further reduce carbon footprints.
Personal vehicles contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. Shared mobility services help combat climate change by encouraging people to use environmentally friendly transport options like electric car-sharing, bike-sharing, and e-scooter programs. Many cities are integrating shared electric vehicle fleets and expanding cycling infrastructure to further reduce carbon footprints. Shared mobility is more than just a transportation alternative—it’s also a way to build stronger communities. Carpooling and ride-sharing services encourage social interactions, connecting people who might not otherwise meet. Bike-sharing and public transport integration enhance mobility access for underserved communities, ensuring that transportation is inclusive and accessible to all.
Shared mobility is more than just a transportation alternative—it’s also a way to build stronger communities. Carpooling and ride-sharing services encourage social interactions, connecting people who might not otherwise meet. Bike-sharing and public transport integration enhance mobility access for underserved communities, ensuring that transportation is inclusive and accessible to all.

 An article from
An article from 

 Volvero, an Italian startup, takes a slightly different approach by integrating advanced technology and a mission-driven focus on sustainability. Unlike traditional car-sharing models, volvero connects owners of underutilized vehicles with drivers who need temporary access to a vehicle. The platform employs AI-driven features to enhance user experience, ensure security, and optimize rental agreements.
Volvero, an Italian startup, takes a slightly different approach by integrating advanced technology and a mission-driven focus on sustainability. Unlike traditional car-sharing models, volvero connects owners of underutilized vehicles with drivers who need temporary access to a vehicle. The platform employs AI-driven features to enhance user experience, ensure security, and optimize rental agreements.


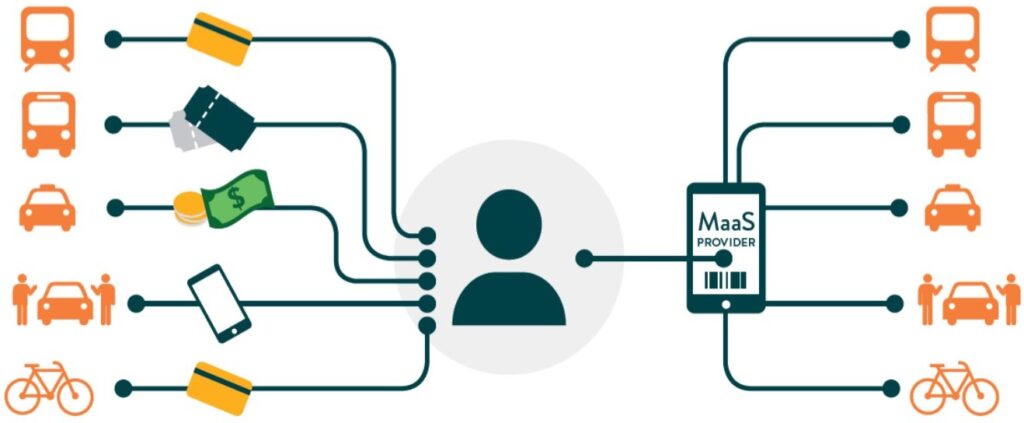
 In 2025, the mobility landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, emphasizing sustainability and technological innovation. Key trends include the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), advancements in charging infrastructure, and the rise of shared mobility solutions. Autonomous driving technologies are enhancing transportation efficiency, while micromobility options like e-scooters and bikes address urban congestion. Additionally, Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) platforms are integrating various transportation modes into seamless user experiences. These developments collectively aim to create a more connected, efficient, and eco-friendly transportation ecosystem.
In 2025, the mobility landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, emphasizing sustainability and technological innovation. Key trends include the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), advancements in charging infrastructure, and the rise of shared mobility solutions. Autonomous driving technologies are enhancing transportation efficiency, while micromobility options like e-scooters and bikes address urban congestion. Additionally, Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) platforms are integrating various transportation modes into seamless user experiences. These developments collectively aim to create a more connected, efficient, and eco-friendly transportation ecosystem. The global shared mobility market is experiencing significant growth, with projections indicating an increase from $343.24 billion in 2024 to $383.92 billion in 2025, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.9%. This upward trajectory is expected to continue, reaching $631.76 billion by 2029 at a CAGR of 13.3%. Key drivers of this expansion include stringent environmental regulations, heightened demand for ride-hailing services, and rising fuel prices. Notable industry players contributing to this growth encompass Didi Chuxing Technology Co., Uber Technologies Inc., and Lyft Inc. As a non-profit shared mobility company, we are committed to advancing sustainable transportation solutions in alignment with these global trends.
The global shared mobility market is experiencing significant growth, with projections indicating an increase from $343.24 billion in 2024 to $383.92 billion in 2025, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.9%. This upward trajectory is expected to continue, reaching $631.76 billion by 2029 at a CAGR of 13.3%. Key drivers of this expansion include stringent environmental regulations, heightened demand for ride-hailing services, and rising fuel prices. Notable industry players contributing to this growth encompass Didi Chuxing Technology Co., Uber Technologies Inc., and Lyft Inc. As a non-profit shared mobility company, we are committed to advancing sustainable transportation solutions in alignment with these global trends. The electric mobility report covers all the major technologies, innovations, and investments in the electric mobility domain. It reveals how trends like hybrid electric vehicle, electric vehicle charging, and power electronics are impacting this eco-friendly mode of transportation. The electric mobility sector is rapidly evolving, focusing on enhancing vehicle design, performance, and affordability. Key trends shaping this landscape include the development of hybrid electric vehicles, advancements in power electronics, and the expansion of electric vehicle charging infrastructure. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, 3D fabrication, and solid-state batteries are poised to drive further innovations, contributing to a more sustainable and efficient transportation ecosystem.
The electric mobility report covers all the major technologies, innovations, and investments in the electric mobility domain. It reveals how trends like hybrid electric vehicle, electric vehicle charging, and power electronics are impacting this eco-friendly mode of transportation. The electric mobility sector is rapidly evolving, focusing on enhancing vehicle design, performance, and affordability. Key trends shaping this landscape include the development of hybrid electric vehicles, advancements in power electronics, and the expansion of electric vehicle charging infrastructure. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, 3D fabrication, and solid-state batteries are poised to drive further innovations, contributing to a more sustainable and efficient transportation ecosystem.

 There’s no denying that cars are a major contributor to both
There’s no denying that cars are a major contributor to both  Shared mobility isn’t just about efficiency—it’s also about
Shared mobility isn’t just about efficiency—it’s also about 


